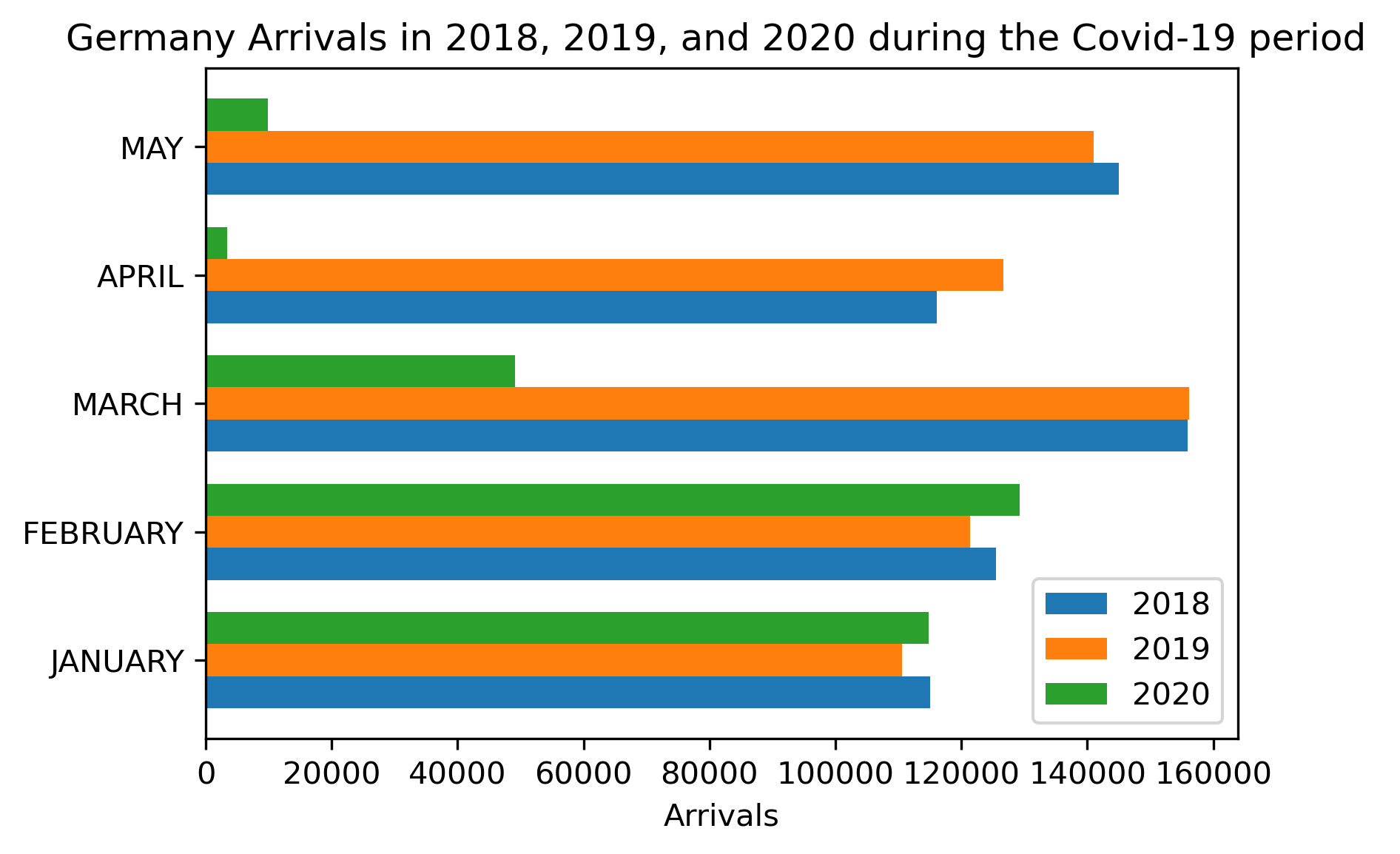Is it possible to find better trends using web-scraping ?
Before using Trends to improve the model, the right question to ask is : what trends keywords should be used ?
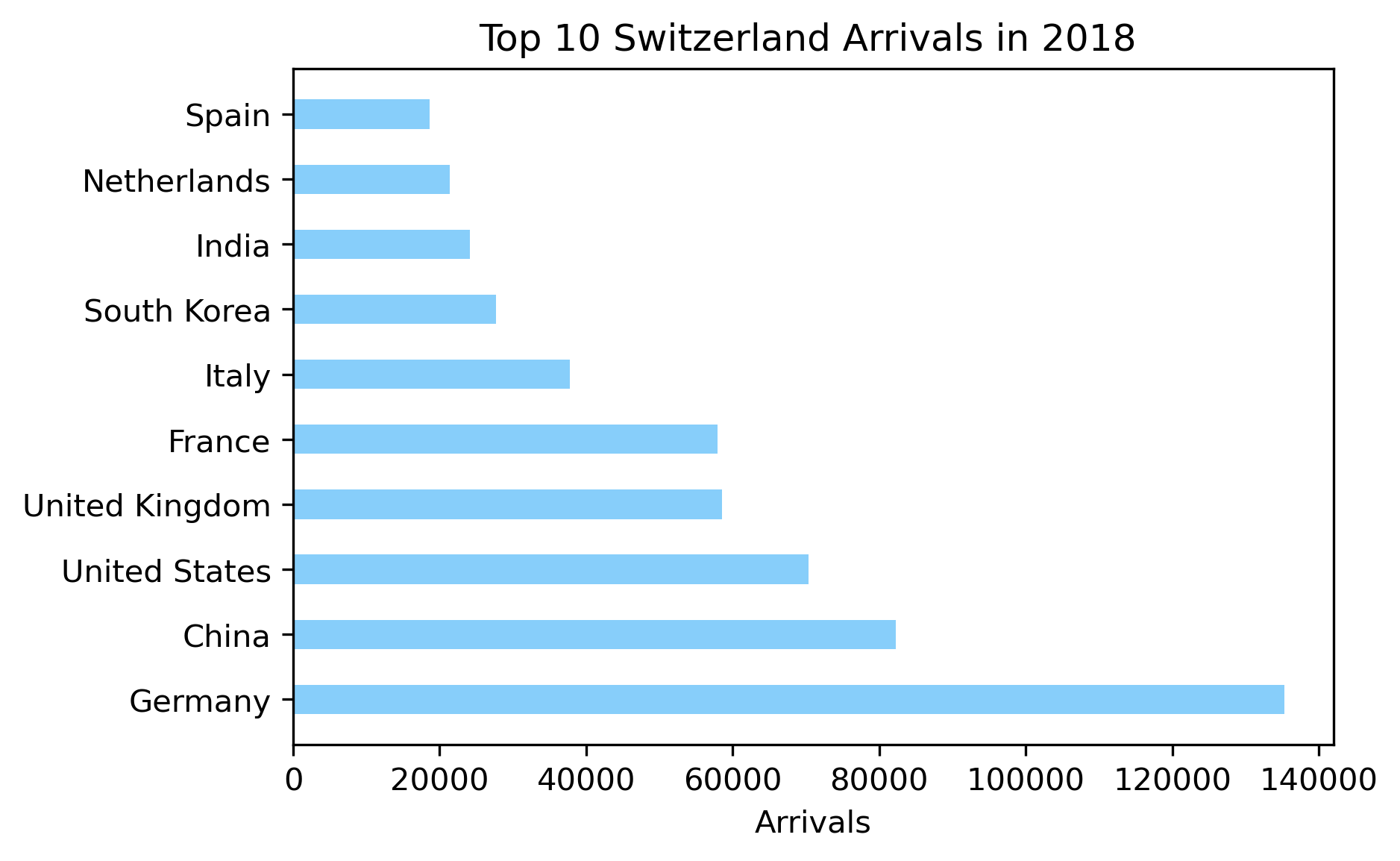
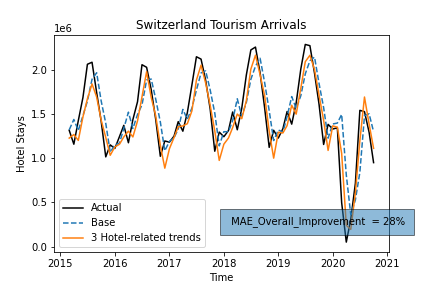
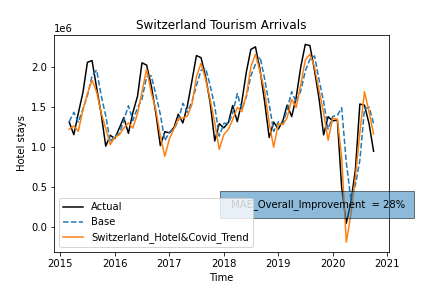
Trends should reflect what people are interested in before coming to Switzerland for a touristic purpose. Thus, articles about tourism are scraped from the web.
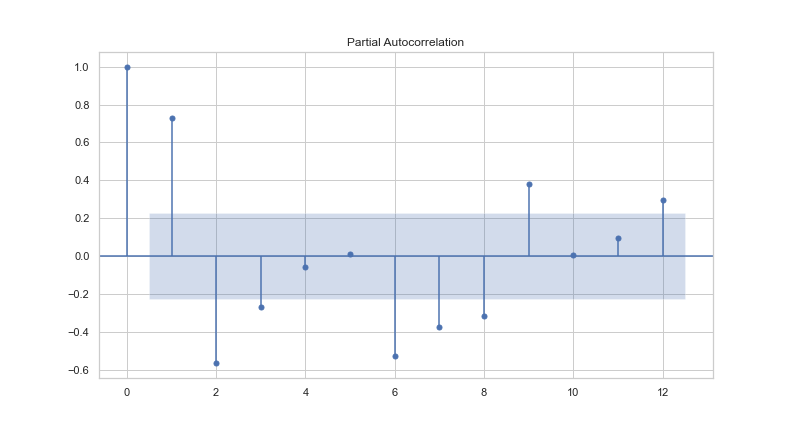
In information retrieval, TFIDF, short for term frequency–inverse document frequency, is a numerical statistic that is intended to reflect how important a word is to a document in a collection or corpus. This method was used to produce a list of trends keywords.
This list of keywords served as a proposition to choose the right features.
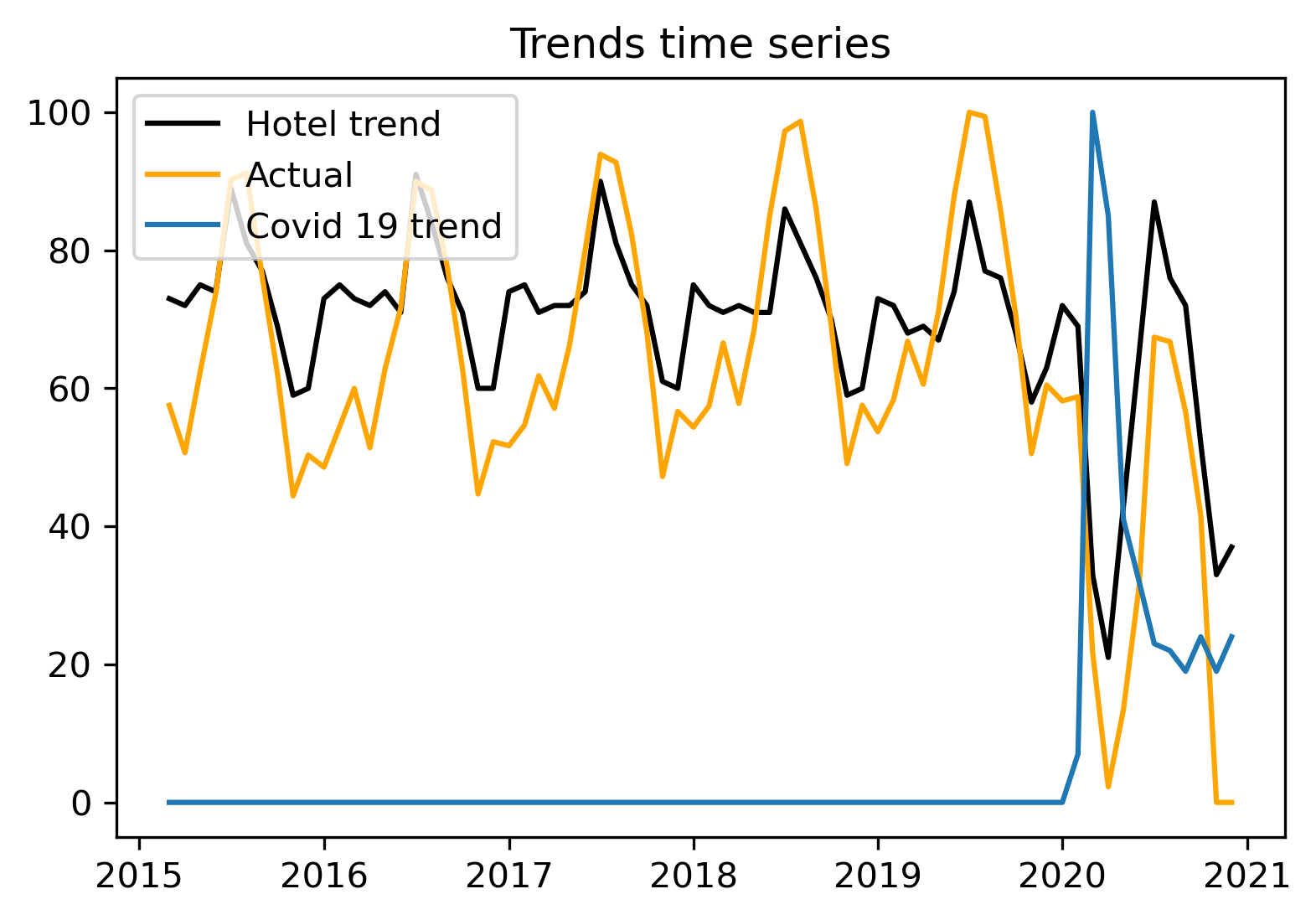
A list of relevant keywords is chosen following some tests. To get the Google Trends by country more relevantly we translate them into respective majority language. Some keywords are relevant rather in some countries than others. Summing these Trends and plotting them allows us to follow the interest in swiss tourism through the years.